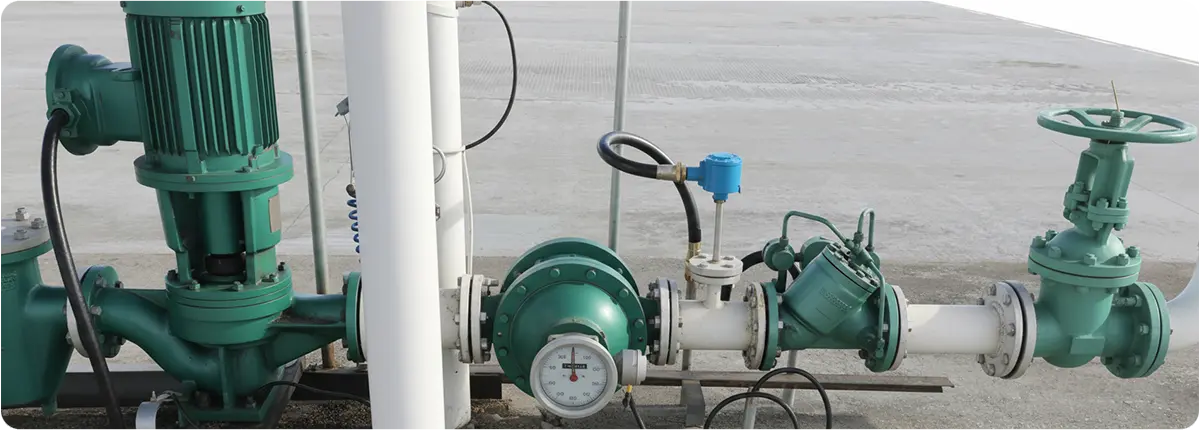
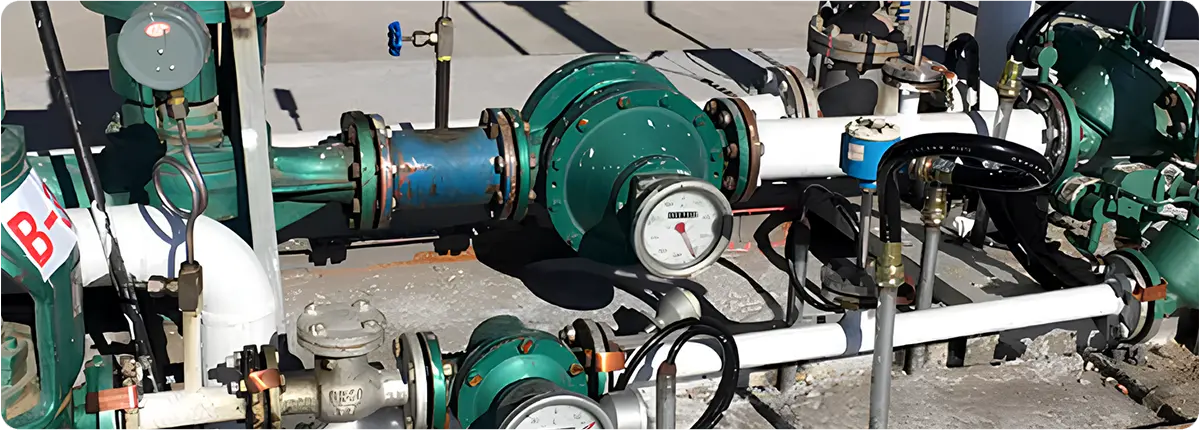
Oval gear flowmeters are one of the most common types of positive displacement flowmeters. They operate on the principle of two oval-shaped gears rotating as fluid passes through them. Each rotation corresponds to a fixed volume, enabling highly accurate volumetric flow measurement. Their reliability with high-viscosity fluids makes them popular in chemical, petroleum, food, and pharmaceutical industries.

WORKING PRINCIPLE
As the fluid flows through the meter, it rotates two intermeshing oval gears. Each rotation displaces a constant amount of fluid, which is detected by sensors. The total flow is calculated by multiplying the number of rotations by the volume per rotation.
Basic equation:
Qv = n · Vc
Qv: volumetric flow rate (m³/s)
n: gear rotation frequency (Hz)
Vc: displaced volume per rotation (m³).
Oval gear flowmeters are particularly effective for low flow rates and viscous fluids.
STRUCTURAL FEATURES
- Body materials: stainless steel, aluminum, cast iron
- Measuring element: two oval-shaped gears
- Output signals: magnetic pickup, pulse, digital signals
- High-pressure resistance
- Low pressure drop and wide measuring range
ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS
Advantages:
- High accuracy (±0.1% – ±0.5%)
- Reliable measurement at low flow rates
- Excellent performance with viscous fluids
- Compact and durable design
Limitations:
- Requires maintenance due to moving parts
- Reduced lifespan with abrasive or particulate fluids
- Limited by high-temperature conditions
APPLICATION AREAS
- Solvent and polymer measurement in chemical industries
- Precise fuel and oil monitoring in petroleum industry
- Syrup, honey, and oil measurement in food industry
- Precise dosing in pharmaceutical industry
- Lubrication systems in energy and automotive sectors
STANDARDS AND CALIBRATION
- OIML R 117: International standard for liquid measuring devices
- ISO/IEC 17025: Calibration laboratory accreditation
- ATEX-certified models for explosive environments
- Regular calibration is necessary to maintain accuracy
CONCLUSION
Oval gear flowmeters provide high accuracy and reliability, making them one of the most trusted solutions for industrial flow measurement. They are especially advantageous for measuring viscous fluids.